Surfing the web is fun and easy, but think what it would be like if you had to type in the IP address of every web site you wanted to view. For example locating a web site would look like this when you type it in: http://24.199.159.59 which would be nearly impossible for most of us to remember. Of course using bookmarks would help but suppose your friend tells you about a cool new web site and tells you to go to 24.199.159.59. How would you remember that? Telling someone to go to “linux-databook.info” is far easier to remember. And, yes, that is the IP address for the DataBook.
The Domain Name System provides the database to be used in the translation from human readable hostnames, such as www.linux-databook.info, to IP Addresses, like 24.199.159.59 so that your Internet connected computers and other devices and access them. The primary function of the BIND software, the Berkeley Internet Name Domain, is that of a domain name resolver which utilizes that database. There is other name resolver software but BIND is currently the most widely used DNS software on the Internet. I will use the terms name server, DNS, and resolver pretty much interchangeably throughout this article.
Without these name resolver services it would be nearly impossible to surf the web as freely and easily as we do. As humans, we tend to do better with names like Linux-DataBook.info, while computers do much better with numbers like 24.199.159.59. So we need a translation service to convert the names that are easy for us to the numbers that are easy for our computers.
In small networks the /etc/hosts file on each host can be used for as a name resolver. Maintaining copies of this file on several hosts can become very time-consuming and errors can cause much confusion and wasted time before they are found. I did this for several years on my own network and it ultimately became too much trouble to maintain even with only the usual 8 to 12 computers I usually have operational. So I ultimately converted to running my own name server to resolve both internal and external hostnames.
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 # Lab hosts 192.168.25.1 server 192.168.25.21 host1 192.168.25.22 host2 192.168.25.23 host3 192.168.25.24 host4 |
Listing 1: A simple hosts file can be maintained by a user to perform the function of a resolver in small networks.
Most networks of any size require centralized management of this service with name services software such as BIND. BIND is called that because it was developed by the University of California Berkeley (UCB) in the early 1980s. Hosts use the Domain Name System (DNS) to locate IP addresses from the names given in software such as web browsers, email clients, SSH, FTP and many other Internet services.
How a name search works
Let’s take look at a simplified example of what happens when a name request for a web page is made by a client service on your computer. For this example, I will use www.Linux-DataBook.info as the website I want to view in my browser. I also assume that there is a local name server on the network, as is the case with my own network.
- First, I type in the URL or select a bookmark containing that URL. In this case, the URL is www.Linux-DataBook.info.
- The browser client, whether it is Opera, Firefox, Chrome, Lynx, Links, or any other browser, sends the request to the operating system.
- The operating system first checks the /etc/hosts file to see if the URL or hostname is there. If so the IP address of that entry is returned to the browser. If not we proceed to the next step. In this case we assume that it is not.
- The URL is then sent to the first name server specified in /etc/resolv.conf. In this case the IP address of the first name server is my own internal name server. For this example, my name server does not have the IP address for www.Linux-DataBook.info cached and must look further afield. So we go on to the next step.
- The local name server sends the request to a remote name server. This can be one of two destination types, one type of which is a forwarder. A forwarder is simply another name server such as the ones at your ISP, or a public name server such as Google at 8.8.8.8 or 8.8.4.4. The other destination type is that of the top level root name servers. The root servers don’t usually respond with the desired target IP address or www.Linux-DataBook.info, they respond with the authoritative name server for that domain. The authoritative name servers are the only ones that have the authority to maintain and modify name data for a domain.The local name server is configured to use the root name servers so the root name server for the .info top level domain returns the IP Address of the authoritative name server for Linux-DataBook.info. That IP address could be for any one of the four (at the time of this writing ) Google name servers since Google Domains is the registrar for linux-databook.info.
- The local name server then sends the query to the authoritative name server which returns the IP address for www.Linux-DataBook.info.
- The browser uses the IP address for www.Linux-DataBook.info to send a request for a web page which is downloaded to my browser.
One of the important side-effects of this name search is that the results are cached for a period of time by my local name server. That means that the next time I, or anyone on my network, wants to access Linux-DataBook.info, the IP Address is probably already stored locally which prevents doing a remote lookup.
The DNS database
The DNS system is dependent upon its database to perform lookups on hostnames to locate the correct IP address. The DNS database is a general-purpose distributed, hierarchical, replicated, database. It also defines the style of hostname used on the Internet, properly called a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
FQDNs consist of complete hostnames such as hornet.example.com and test1.example.com. FQDNs break down into three parts.
- The top level domain names (TLDN) such as .com, .net, .biz, .org, .info, .edu, and so on, provide the last segment of a FQDN. All TLDNs are managed on the root name servers. Aside from the country top level domains such as .us, .uk, and so on, there were originally only a few main top level domains. As of February, 2017 there are 1528 top level domains.
- The second level domain name is always immediately to the left of the top level domain when specifying a hostname or URL. So names like redhat.com, Linux-DataBook.info, getfedora.org, and example.com provide the organizational address portion of the FQDN.
- The third level of the FQDN is the hostname portion of the name. So the FQDN of a specific host in a network would be something like host1.example.com.
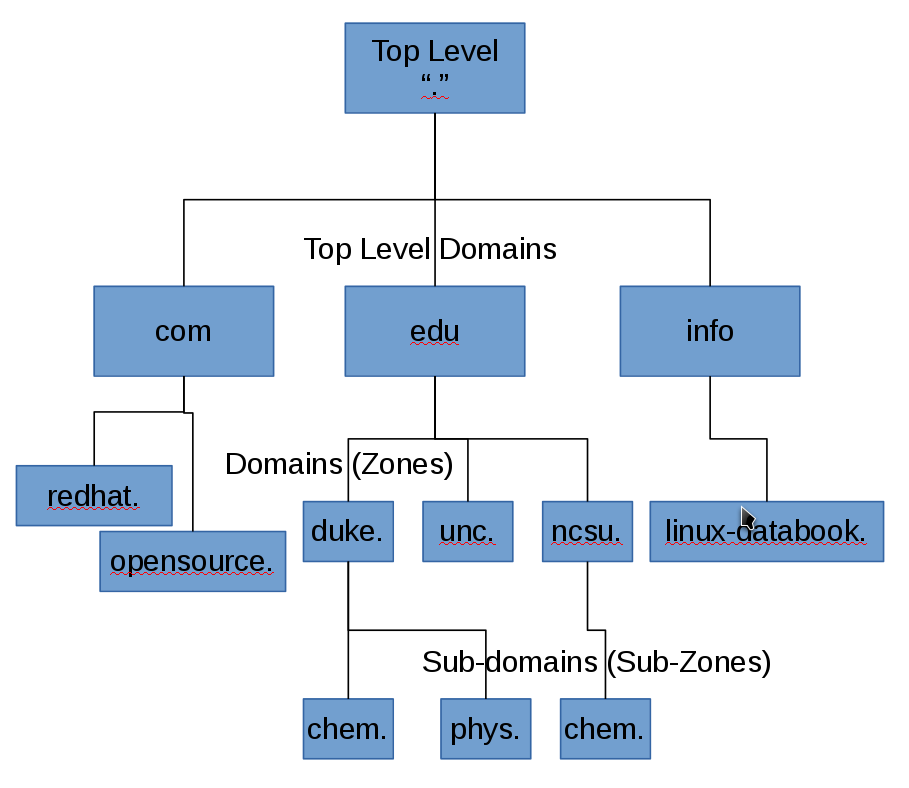
Figure 1: A simplified representation of the DNS database hierarchical structure.
Figure 1 shows a simplified diagram of the DNS database hierarchy. The “top” level, which is represented by a single dot (.) has no real physical existence. It is a device for use in DNS zone file configuration to enable an explicit end stop for domain names. A bit more on this later.
The true top level consists of the root name servers. These are a limited number of servers that maintain the top level DNS databases. The root level may contain the IP Addresses for some domains and the root servers will directly provide those IP addresses where they are available. In other cases the root servers provide the IP addresses of the authoritative server for the desire domain.
For example, assume we want to browse www.Linux-DataBook.info. Our browser makes the request of the local name server which does not contain that IP address. My local name server is configured to use the root servers when an address is not found in the local cache, so it sends the request for www.Linux-DataBook.info to one of the root servers. Of course the local name server must know how to locate the root name servers so it uses the /var/named/named.ca file which contains the names and IP addresses of the root name servers. The named.ca file is also known as the hints file.
In this example, the IP address for www.Linux-DataBook.info is not stored by the root servers. The root server uses its database to locate the name and IP address of the authoritative name server for www.Linux-DataBook.info.
The local name server queries the authoritative name server which returns the IP address of www.Linux-DataBook.info. The local name server then responds to the browser’s request and provides it with the IP address. The authoritative name server for Linux-DataBook.info contains the zone files for that domain.
# dig www.linux-databook.info
; <<>> DiG 9.10.4-P6-RedHat-9.10.4-4.P6.fc25 <<>> www.linux-databook.info
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 34962
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 4, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.linux-databook.info. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.linux-databook.info. 3600 IN CNAME wally1.linux-databook.info.
wally1.linux-databook.info. 3600 IN A 24.199.159.59
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
linux-databook.info. 86400 IN NS ns-cloud-a1.googledomains.com.
linux-databook.info. 86400 IN NS ns-cloud-a2.googledomains.com.
linux-databook.info. 86400 IN NS ns-cloud-a4.googledomains.com.
linux-databook.info. 86400 IN NS ns-cloud-a3.googledomains.com.
;; Query time: 633 msec
;; SERVER: 192.168.0.51#53(192.168.0.51)
;; WHEN: Wed Apr 19 21:41:22 EDT 2017
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 210
|
Listing 2: The results of a dig command displays not only the IP address of the desired host, but it also shows the authoritative servers, their IP addresses, and the server that actually fulfilled the request.
Listing 2, above, shows the results of a dig command that obtains the DNS information for www.Linux-DataBook.info. The dig command is a powerful tool that can tell us a lot of information about the DNS configuration for a host. The dig command returns the actual records from the DNS database and displays the results in four main sections. Refer to Listing 2 as you read the descriptions of these sections.
The first section is the question section. For our example, it states that we are looking for the A record of “www.Linux-DataBook.info.”. Notice the dot at the end of the top level domain name. This indicates that .info. is the final domain name component in the hostname.
The answer section shows an A record. A records are the primary name resolver records and there must be an A record which contains the IP address for each host.
Results for some domains may also show one or more CNAMEs. CNAME stands for Canonical Name and this record type is an alias for the A record and points to it. It is not typical practice to use “www” as the hostname for a web server. It is common to see a CNAME record that points to the A record of the FQDN. However that is not quite the case here. Notice that the A record for Linux-DataBook.info. does not have a hostname associated with it. It is possible to have a record that applies to the domain as a whole as is the case here.
The authority section lists the authoritative name servers for the Linux-DataBook.info domain. In this case those are the Google name servers. Notice that the record type is NS for these entries.
There may also be an additional section that lists the A records for the authoritative name servers.
Following the additional or authority section you can find some additional interesting information, including the IP address of the server that returned the information shown in the results. In this case it was my own internal name server.
DNS Client configuration
Most computers need little configuration to enable them to access name services. That usually consists of adding the IP addresses of one to three name servers to the /etc/resolv.conf file. And that is typically performed at boot time on most home and laptop computers because they are configured using the DHCP protocol which provides them with their IP address, gateway address, and the IP addresses of the name servers.
For hosts that are configured statically, the resolv.conf file is usually generated during installation from information entered by the sysadmin doing the install. In current Red Hat based distributions and others that use NetworkManager to manage network configuration and to perform connection management, the static information such as name servers, gateway, and IP address are all stored in the interface configuration files located in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts.
It is possible to override the defaults provided to a host by adding that information to the interface configuration file. For example I sometimes add my preferred name servers to the interface configuration files on my laptop and netbook. Many of the name servers provided by remote connections in public places such as hotels, coffee shops, and even friends’ personal WiFi connections, can be unreliable and in some cases can use forwarders that intentionally censor results or redirect queries to pages of advertisements. So I always insert the Google public name servers in my interface configuration files. Refer to my article How to configure networking in Linux for information about the interface configuration files.
Also be aware that NetworkManager creates an interface configuration file for each WiFi network it connects with. The configuration files are named for the SSID of the network. Be sure to add the desired name server entries to the correct file.
Some of the interface configuration files that have been created on my laptop by NetworkManager in the last few months are listed below.
- ifcfg-enp0s25 – this is the configuration file for the wired network
- ifcfg-FBI-DHS.TF1_EXT
- ifcfg-HOME-14A2
- ifcfg-linksys
- ifcfg-LinuxDude
- ifcfg-MomsPlace
- ifcfg-FBI-van
- ifcfg-PointSourceGuest
- ifcfg-Red_Hat_Guest
- ifcfg-Sands_3_hoa1
- ifcfg-Sheraton_Raleigh_Guest_Access
- ifcfg-SM-CLC1
- ifcfg-xfinitywifi
And no, I do not have any connection with the FBI. Someone I know who shall remain nameless has an interesting sense of humor and enjoys making the neighbors nervous.
DNS record types
There are a number of different DNS record types and I want to introduce some of the more common ones here. My next article will describe how to create your own name server using BIND and will use many of these record types to build your name server. These record types are used in the zone files that comprise the DNS database. One common field in all of these records is “IN” which specifies that these are INternet records. There is no other type of record at this time.
You can find a complete list of DNS record types here.
SOA
SOA is the Start Of Authority record. It is the first record in any forward or reverse zone file and it identifies this as the authoritative source for the domain it describes. It also specifies certain functional parameters. A typical SOA record looks like the sample below.
@ IN SOA epc.example.com root.epc.example.com. (
2017031301 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ; expire
3H ) ; minimum
|
Listing 3: The SOA record defines this as the authoritative source for the domain.
The first line of the SOA record contains the name of the server for the zone and the zone administrator, in this case root.
The second line is a serial number. In this example I use the date in YYYYMMDDXX format where XX is a counter. So the serial number in the SOA record above represents the first version of this file on March 13, 2017. This format ensures that all changes to the serial number are incremented in a numerically sequential manner. That is important because secondary name servers, also known as slave servers, only replicate from the primary server when the serial number of the zone file on the primary is greater than the serial number on the secondary. Be sure to increment the serial number when you make changes or the secondary server will not sync up with the modified data.
The rest of the SOA record consists of various times that secondary servers should perform a refresh from the primary and wait for retries if the first refresh fails. It also defines the amount of time before the zone’s authoritative status expires.
Times all used to be specified in seconds, but recent versions of BIND allow other options defined with W=week, D=day, H=hour, and M=minute. Seconds are assumed if no other specifier is used.
$ORIGIN
The $ORIGIN record is like a variable assignment. The value of this variable is appended by the BIND program to any name in an A or PTR record that does not end in a period (.) in order to create the FQDN for that host. This makes for less typing because the zone administrator only has to type the host name portion and not the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for each record.
$ORIGIN example.com. |
Listing 4: A typical origin record.
Also, the @ symbol is used as a shortcut for this variable and any occurrence of @ in the file is replaced by the value of $ORIGIN.
NS
The NS record specifies the authoritative name server for the zone. Note that both names in this record end with periods so that “.example.com” does not get appended to them. This record will usually point to the local host by its fully qualified domain name.
example.com. IN NS epc.example.com. |
Listing 5: The name server record.
Note that the host, epc.example.com, must also have an A record in the zone. The A record can point to the external IP address of the host or to the localhost address, 127.0.0.1.
A
The A record is the Address record type that specifies the relationship between the host name and the IP address assigned to that host. In the example below, the host test1 has IP address 192.168.25.21. Note that the value of $ORIGIN is appended to the name test1 because test1 is not an FQDN and does not have a terminating period in this record.
test1 IN A 192.168.25.21 |
Listing 6: the A record specifies the IP address for a host in the zone file.
The A record is the most common type of DNS database record.
CNAME
The CNAME record is an alias for the name in the A record for a host. For example, the hostname server.example.com might serve as bother the web server and the mail server. So there would be one A record for the server, and possibly two CNAME records as shown below.
server IN A 192.168.25.1 www IN CNAME server mail IN CNAME server |
Listing 7: CNAME records provide aliases for a host with a given IP address.
Lookups with the dig command on www.example.com and mail.example.com will return the CNAME record for mail or www and the A record for server.example.com.
PTR
The PTR records are to provide for reverse lookups. This is when you already know the IP address and need to know fully qualified host name. For example many mail servers do a reverse lookup on the alleged IP address of a sending mail server to verify that the name and IP address given in the email headers match. PTR records are used in reverse zone files. Reverse lookups can also can be used when attempting to determine the source of suspect network packets.
Be aware that not all hosts have PTR records, and many ISPs create and manage the PTR records so reverse lookups may not provide the needed information.
MX
The MX record defines the Mail eXchanger, i.e., the mail server for the domain example.com. Notice that it points to the CNAME record for the server in the example above. Note that both example.com names in the MX record terminate with a dot so that example.com is not appended to the names.
; Mail server MX record
example.com. IN MX 10 mail.example.com.
|
Listing 8: MX records define Mail eXchangers (servers) for a domain.
Domains may have multiple mail servers defined. The number “10” in the above MX record is a priority value. Other servers may have the same priority or different ones. The lower numbers define higher priorities. So if all mail servers have the same priority they would be used in round robin fashion. If they have different priorities, the mail delivery would first be attempted to the mail server with the highest priority – the lowest number – and if that mail server did not respond, delivery would be attempted to the mail server with the next highest priority.
Other Records
There are other types of records that you may encounter in the DNS database. One type, the TXT records, are used to record comments about the zone or hosts in the DNS database. TXT records can also be used for DNS Security. The rest of the DNS record types are outside the scope of this article.
Conclusion
Name services is a very important part of making the Internet easily accessible. It binds the myriad disparate hosts connected to the Internet into a cohesive unit that makes it possible to communicate with the far reaches of the planet with ease. It has a complex distributed database structure that is perhaps even unknowable in its totality, yet that can be rapidly searched by any connected device to locate the IP address of any other device that has an entry in that database.
If you are a system administrator on a network of almost any size, you may find it helpful to know how to build your own name server. I describe how you can do that in the article, Build your own domain name server.
Resources
- Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
- Start of Authority (SOA) record
- List of DNS Record Types
- Common DNS records and their uses